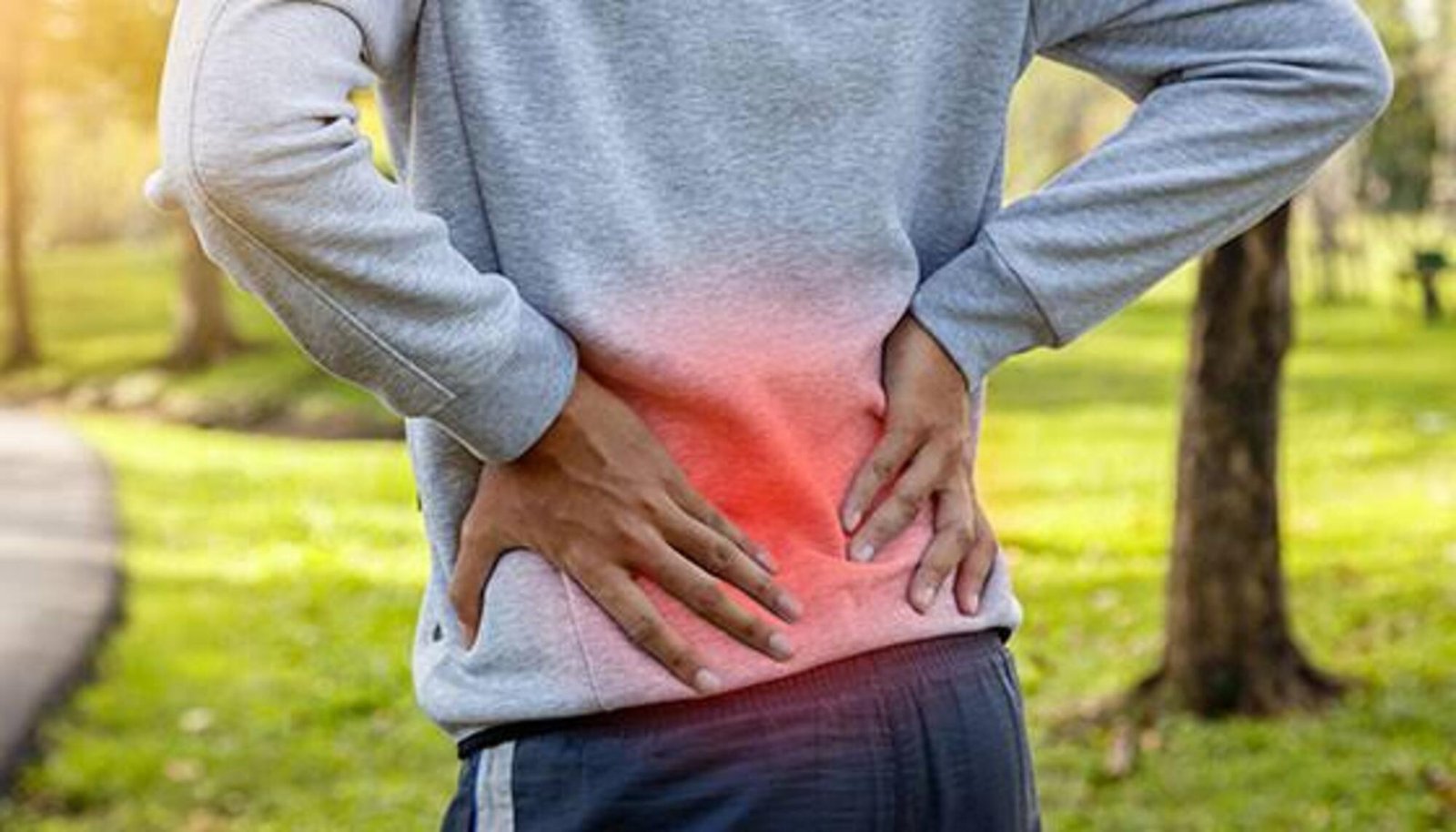
Back pain is a typical region behind non-attentive during work and looking for medical treatment. It tends to be uncomfortable and feels stiff.
It can result from injury, action and some medical conditions. Back pain can influence people of all ages, for various reasons. As many people get older they may suffer from back problems because of various reasons like past occupation and degenerative disc disease.
Lower back pain might be connected to the bony lumbar spine, the disc between the vertebrae, tendons around the spine and discs, spinal cord and nerves, lower back muscles, stomach and pelvic internal organs, and the skin around the lumbar area.
Pain in the upper back might be because of problems of the aorta, cancer in the chest, and spine inflammation.
Types of Back pain
The human back is made of complicated structures of muscles, tendons, ligaments, disk, and bones, which work together to help the body and enables us to move around.
The segment of the spine is padded with ligament-like cushions called disks.
Issues with any of these parts can prompt back pain. Now and again of back pain.
Damage can result from strain, medical conditions, and poor posture, among others.
Strains
The muscles and tendons in the back can stretch or tear because of abundance action. Symptoms include pain and tiredness in the lower back, just as muscle stiffness. Rest and physiotherapy treatment are solutions for these signs.
Disc injury
The disc in the back is prone to injury. This danger increments with age. The outside of the circle can tear or herniate.
A herniated disc, which is otherwise called a slipped or cracked plate happens when the ligament encompassing the plate pushes against the spinal cord or nerve cord. The cushion that sits between the spinal vertebrae stretches out its normal position
This can bring about the pressure of the nerve root as it exits from the spinal rope and through the vertebral bones. Disk injury as a rule happens unexpectedly after lifting something or twisting the back. unlike back strain, pain from a disc injury typically goes over 72 hours.
Sciatica
Sciatica can happen with a herniated disc if the disc pushes on the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve associates the spine to the legs. Subsequently, sciatica can cause pain in the legs and feet. This aggravation feels like a burning or a tingling sensation.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the point at which the spinal column narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves.
Spinal stenosis is most ordinarily because of degeneration of the disc between the vertebrae. The outcome is the pressure of the nerve roots or spinal cord by bony spurs or delicate tissues, like discs.
The strain on the spinal nerves causes side effects, for example,
Numbness
Cramping
Weakness
You may feel these side effects anyplace in the body. Many people with spinal stenosis notice their side effects while standing and walking.
Abdominal spine curvatures
Scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis are all conditions that cause abnormal curvatures in the spine.
These are innate conditions that are normally first analysed during childhood or puberty. The abnormal curvatures cause pain and weak posture since it places pressure on:
- muscles
- ligaments
- tendons
- vertebrae
Movement and posture
Acquiring an extremely hunched sitting position when using a laptop computer can result in increased back and shoulder pain over time.
Back pain can likewise result from some daily exercises or weak posture.
Examples include:
Twisting
Coughing and sneezing
muscle tension
over-stretching
Over bending for long periods
pushing, pulling, lifting, or conveying something
standing or sitting for extensive stretches
stressing the neck forward, like when driving or using a PC
long driving without a break.
Sleeping on a cushion that doesn’t support the body and keep the spine straight
Risk factors
The accompanying factors are connected to a higher risk of developing lower back pain:
- Occupational activities
- pregnancy
- poor physical fitness
- Older age
- heavy weight lifting
- smoking
- Strenuous physical exercise or work, even if done inaccurately
Genetics factors
Medical conditions like joint pain and cancer.
Lower back pain likewise will in general be more normal in women than in men, potentially because of hormonal changes. Stress, tension, and state of mind problems have additionally been connected to back pain.
Diagnosis
A doctor can normally analyse back pain after getting some information about Symptoms and completing a physical assessment.
An imaging scan and different tests might be required if:
back pain seems to result from a physical injury
there might be a hidden reason that needs treatment. The pain continues over a long period
An X-ray, MRI, or CT scan can give data about the condition of the soft tissues in the back.
X-rays can show the arrangement of the bones and detect signs of arthritis or broken bones, however, they may not show damage in the muscles, spinal cord, nerves, or disc.
MRI or CT can tell us about herniated discs or issues with tissue, ligaments, nerves, tendons, veins, muscles, and bones.
Bone recognise bone cancers or bone breaks caused by osteoporosis. A radioactive substance or tracer is infused into a vein. The tracer gathers in the bones and helps the doctor with distinguishing bone issues with the aid of a special camera.
Electromyography or EMG measures the electrical driving forces created by nerves because of muscles. This can confirm nerve pressure, which might happen with a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
The doctor may also ask to do a blood test in case an infection is suspected.
Back Pain Treatments
Back pain is normally gone while resting and home cures, yet but for some medical conditions treatments are necessary.
Home medicines
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relief medications, normally nonsteroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAID), like ibuprofen, can help in lowering pain. Using a hot pad or an ice pack to the painful region may likewise lower pain.
Resting from difficult activity can help, yet moving around will ease stiffness, decrease pain and prevent muscles from weakening.
Medical Treatment
Drug: Back pain that doesn’t react well to OTC painkillers might require a solution NSAID. Codeine or hydrocodone, which are opiates(narcotics), might be recommended for short periods. These require close observing by the doctor. In many cases, muscle relaxants might be used.
Antidepressants, like amitriptyline, might be recommended, yet research is continuous at to their viability, and the proof is conflicting.
Physical Therapy: Applying heat, ice, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation — as same as muscle-release techniques to the back muscles and soft tissues — may assist with easing pain.
As the pain improves, the physical advisor might tell some flexibility and strength exercises for the back and stomach muscles. Techniques for further improving posture may likewise help.
The patient will be urged to rehearse the methods consistently, even after the pain has gone, to prevent further back pain.
Cortisone infusions: If different alternatives are not workable, these might be infused into the epidural space, around the spinal cord. Cortisone is an anti-inflammatory drug. It prevents inflammation around the nerve cord. Infusions may likewise be used to numb regions thought to cause the pain.
Traction: Pulleys and weight are used to stretch the back. This might result in a herniated disc moving once again in the position. It can likewise ease help yet just while traction is applied.
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT): CBT can assist with managing chronic back pain by encouraging better approaches to thinking. It might include relaxation strategies and methods of keeping to maintain a positive attitude.
Botox: Botox (botulism poison), as indicated by some early examinations, is thought to decrease pain by deadening hyper-extended muscles in spasms. These infusions are effective for around 3 to 4 months.
Back Pain Prevention
Steps to take to bring down the risk of developing back pain mainly addressing some of the risk factors.
Back pain exercises: Regular exercise helps develop muscles and control body weight. low-level aerobics exercises can help heart health without stressing or jerking the back. Before beginning any activity session, consult with a medical care professional.
There are two principal kinds of activity that individuals can do to decrease the risk of back pain:
Core strengthening exercises work the stomach and back muscles, assisting with strengthening muscles that protect the back.
Stretching exercises further help core flexibility, including the spine, hips, and upper legs.
Diet: Make sure your eating regimen includes sufficient calcium and vitamin D, as these are required for bone health. A balanced eating regimen likewise assists control with bodyweight: The overweight person carries weight and where they convey it influences the danger of developing back pain. The distinction in back pain risk among obsess and normal-weight people quite ma atter of people who carry their weight in the stomach region versus the backside and hip region likewise a more serious risk.
Posture when standing: Make sure you have a neutral position. Stand upright, head looking forward, back straight, and equilibrium your weight equitably on the two feet. Keep your legs straight and your head by your spine.
Posture when sitting: A decent seat for working should have great back help, armrests and a turn base. When sitting, attempt to keep your knees and hips level and keep your feet level on the floor, or use footstools. You should perfectly be able to sit upright without providing little help to your back. In case you are using a keyboard, ensure your elbows are at the right points and that your forearms are in level horizontal.
Bed: You should have a sleeping mattress that keeps your spine straight, while at the same time supporting the weight of your shoulders and buttocks. Used a cushion, yet not one that powers your neck into a steep angle.