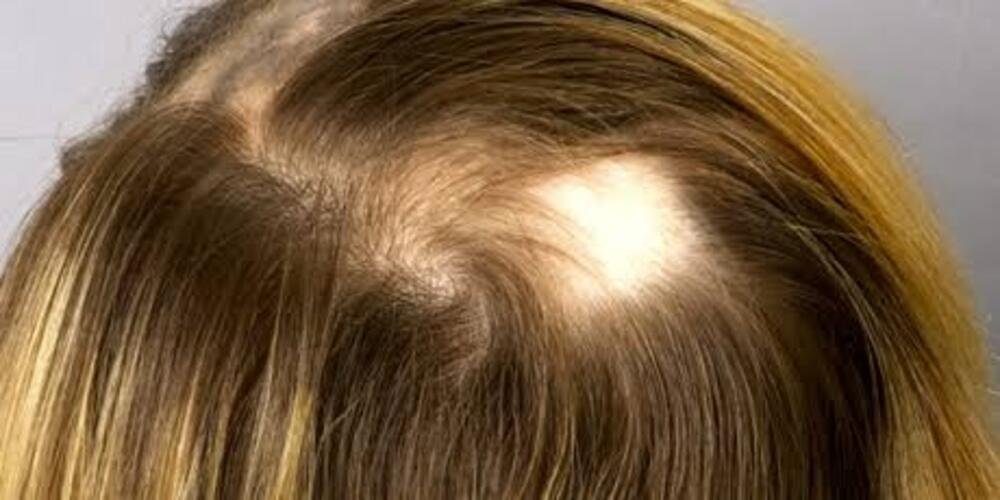
Explore our simple guide on alopecia, breaking down hair loss into easy insights. Discover types, causes, and practical confidence-boosting solutions. Whether it’s your journey or supporting someone else’s, we’re here for you. Join us in understanding and navigating alopecia with simplicity. Find quick insights and easy tips designed to make your experience lighter and more manageable.
Causes Of Alopecia
1.Genetics: Inherited factors play a significant role in alopecia, with a family history of the condition increasing the risk.
2.Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can trigger alopecia.
3.Medical Conditions: Certain illnesses, like autoimmune diseases and thyroid disorders, may contribute to hair loss.
4.Stress and Trauma: Physical or emotional stress can lead to alopecia, with severe stressors potentially causing a temporary condition called telogen effluvium.
5.Medications and Treatments: Some drugs, like chemotherapy medications, may result in hair loss as a side effect.
6.Infections: Fungal or bacterial infections of the scalp can contribute to certain types of alopecia.
Symptoms Of Alopecia
- Patchy Hair Loss: The most common symptom, characterized by distinct areas of hair loss on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Sudden Hair Thinning: Rapid thinning of hair, especially in specific areas, can be an early sign of alopecia.
- Complete Baldness: In some cases, alopecia may progress to total hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or the entire body (alopecia universalis).
- Changes in Nail Health: Brittle or pitted nails might accompany certain types of alopecia.
- Itching or Discomfort: Some individuals may experience itching or discomfort in areas where hair loss is occurring.
- Regrowth with White or Gray Hair: Hair may regrow, but in some cases, it could be white or gray instead of the original color.
- Exclamation Mark Hairs: Short, broken hairs resembling exclamation points near the scalp might be visible in areas affected by alopecia areata.
Types Of Alopecia
1.Alopecia Areata: Characterized by sudden, patchy hair loss on the scalp or body, often linked to an autoimmune response.
2.Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, it’s a hereditary condition causing gradual hair thinning.
3.Alopecia Totalis: Involves the complete loss of hair on the scalp.
4.Alopecia Universalis: Results in total hair loss on the entire body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
5.Telogen Effluvium: Triggered by significant stress or hormonal changes, leading to excessive shedding of hair in its resting phase.
6.Scarring Alopecia: Causes permanent hair loss due to inflammation and scarring of hair follicles.
7.Traction Alopecia: Caused by repeated pulling or tension on the hair, commonly due to tight hairstyles.
8.Trichotillomania: A psychological condition where individuals compulsively pull out their own hair, leading to noticeable patches of baldness.
Diagnosis Of Alopecia
1.Medical History: A thorough discussion about personal and family medical history, including any history of autoimmune diseases or other conditions related to hair loss.
2.Physical Examination: A close examination of the scalp and affected areas to assess the pattern and severity of hair loss.
3.Pull Test: Gently pulling on several hairs to observe the number of strands that come out, helping to identify conditions like telogen effluvium.
4.Blood Tests: Checking for specific markers or deficiencies that could contribute to hair loss, such as iron levels or thyroid function.
5.Biopsy: In some cases, a small skin biopsy may be performed to examine a tissue sample under a microscope, aiding in the diagnosis of scarring alopecia.
6.Scalp Imaging: Using tools like a microscope to examine the scalp closely, which can provide additional insights into the health of hair follicles.
7.Allergy Tests: In cases of suspected allergic reactions, patch tests may be conducted to identify potential triggers.
Treatment For Alopecia
1.Topical Treatments: Minoxidil is a common over-the-counter topical treatment that can promote hair growth for certain types of alopecia.
2.Corticosteroids: Applied topically or injected, corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth, especially in cases of alopecia areata.
3.Anthralin: A topical medication that alters skin cell function, often used for treating mild to moderate cases of alopecia areata.
4.Immunotherapy: This involves applying chemicals like diphencyprone to the scalp to induce an allergic reaction, potentially stimulating hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
5.Oral Medications: For some types of alopecia, oral medications like finasteride or corticosteroids may be prescribed to address underlying causes.
6.Light Therapy: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or phototherapy can stimulate hair growth in certain cases.
7.Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles.
8.Hair Transplantation: In cases of permanent hair loss, surgical procedures like hair transplantation can be considered.
Prevention For Alopecia
While complete prevention of alopecia may not be possible in some cases, there are steps to minimize the risk and promote overall hair health:
1.Maintain a Balanced Diet: Ensure you’re getting essential nutrients like iron, vitamins A and D, and protein, which are crucial for healthy hair.
2.Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques, as chronic stress can contribute to certain types of alopecia.
3.Gentle Hair Care: Avoid tight hairstyles, excessive heat styling, and harsh chemical treatments to prevent damage to hair follicles.
4.Regular Scalp Massage: Promote blood circulation with regular, gentle scalp massages to support hair health.
5.Avoid Pulling or Tugging: Be mindful of hairstyles that involve pulling or tugging on the hair, as this can contribute to traction alopecia.
6.Prompt Treatment of Infections: Address scalp infections promptly to prevent potential damage to hair follicles.
7.Limit Use of Harsh Chemicals: Minimize exposure to harsh chemicals in hair products and dyes that could irritate the scalp.
8.Regular Checkups: Keep up with routine health checkups to address any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to alopecia.
Outlooks
Maintaining healthy hair involves a combination of lifestyle practices, stress management, and gentle care. While some forms of alopecia may not be entirely preventable, adopting a balanced diet, minimizing stress, and being mindful of hair care practices can contribute to overall hair health. Early detection and consultation with a healthcare professional are crucial if symptoms of alopecia arise. Remember, everyone’s journey is unique, and seeking support from healthcare providers and support communities can make facing alopecia more manageable. Embrace a holistic approach, prioritize self-care, and empower yourself on the path to hair wellness.