Living with diabetes offers daily challenges, from monitoring blood sugar levels to managing medications and making lifestyle adjustments. Despite these challenges, the question remains: can diabetes be cured? For millions worldwide struggling with this chronic condition, hope for a cure is a source of light among their fears. We’ll examine the challenges of managing diabetes as well as the most recent developments in the field, to answer the important question: is diabetes curable? For people managing diabetes and hoping for a cure, you must understand the disease’s course, available therapies, and recent promising developments in science. Let’s find out together whether diabetes can be cured.
Understanding Diabetes?

Diabetes is a long-term illness that weakens the body’s capacity to control blood sugar levels.
The Role of Insulin: The pancreas, a gland behind your stomach, produces insulin. When you eat, your blood sugar levels rise, prompting the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin then helps shepherd glucose into your cells for energy.
What Goes Wrong in Diabetes: In diabetes, this process is disrupted. Diabetes comes in two primary forms: type 1 and type 2.
- Type 1 Diabetes: In type 1 diabetes, the pancreatic cells that produce insulin are accidentally attacked and destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells for energy, hence benefiting in blood sugar regulation. High blood sugar is caused by an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream due to insufficient insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This kind of diabetes is brought on by an insufficient or resistant response to insulin by the body, which makes it difficult for normal blood sugar levels to be maintained. Genetics, poor diet, obesity, and physical inactivity are risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Can diabetes be cured ?

Although there is currently no known cure, particularly for type 1 diabetes, developments provide promise for better treatment and even a possible reversal for type 2.
Type 1 Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Because of this, insulin therapy is necessary throughout the life of a person with type 1 diabetes. Although there isn’t yet a treatment for type 1 diabetes, scientists are looking into a number of options, such as:
- Pancreas Transplantation: Transplanting a healthy pancreas can cure type 1 diabetes, but it is a complex procedure with significant risks.
- Islet Cell Transplantation: Islet cells are responsible for producing insulin. Transplanting these cells into the body can help restore normal insulin production.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy aims to stop the immune system from attacking insulin-producing cells in type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. While type 2 diabetes can’t always be cured, it can often be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medication. In some cases, type 2 diabetes can even be reversed with:
- Weight Loss: Losing weight through diet and exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Medication: In addition to lifestyle changes, medications such as metformin, insulin, and other oral medications may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
Current Treatments for Diabetes

Managing diabetes effectively involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and ongoing monitoring. While a definitive cure for diabetes is still not available, current treatments focus on controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Here are the main treatments for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Medications
- Insulin Therapy: Current Treatments for Diabetes: Essential for people with type 1 diabetes and sometimes necessary for those with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy helps regulate blood sugar levels by replacing the insulin the body no longer produces or does not produce enough of.
- Oral Medications: For type 2 diabetes, medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and SGLT2 inhibitors help improve insulin sensitivity, increase insulin production, or reduce glucose absorption.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: A healthy, balanced diet is crucial for managing diabetes. Eating foods low in sugar and high in fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, helps control blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly impact blood sugar control, especially for those with type 2 diabetes.
Monitoring
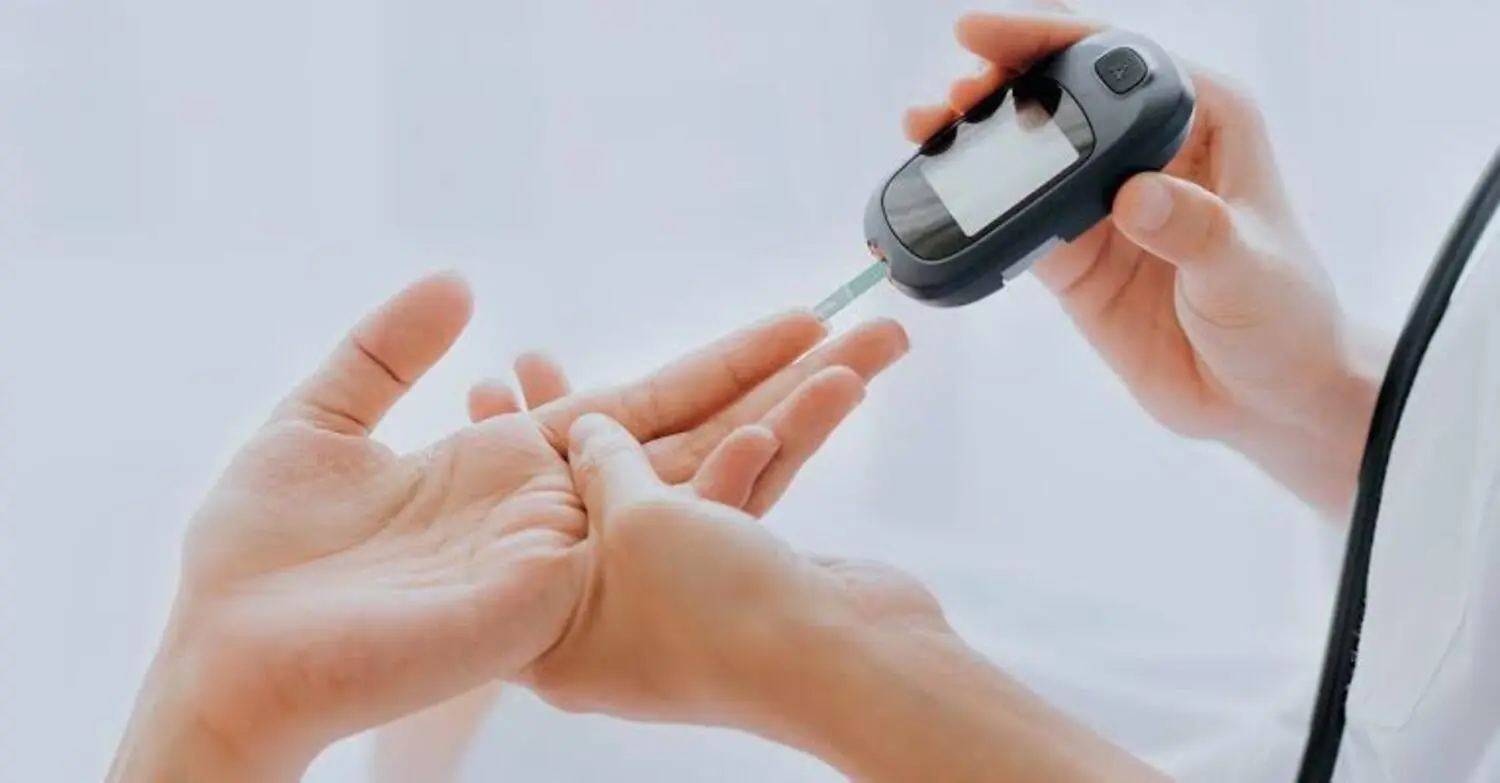
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes. This helps individuals adjust their treatment plans and prevent complications.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs provide real-time blood sugar readings and trends, helping individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their treatment.
Advanced Treatments
- Bariatric Surgery: For obese individuals with type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery can lead to significant weight loss and improved blood sugar control, with some cases showing potential diabetes remission.
- Artificial Pancreas: This system automatically monitors blood glucose levels and delivers the appropriate amount of insulin, mimicking a healthy pancreas and improving blood sugar control.
Emerging Therapies
- Stem Cell Therapy: Researchers are investigating the use of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, offering potential for a future cure.
- Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR are being explored to correct genetic defects that cause type 1 diabetes.
- Immunotherapy: Aims to modify the immune system to prevent it from attacking insulin-producing cells in type 1 diabetes.
While the question “can diabetes be cured?” remains, current treatments have significantly improved the quality of life for people with diabetes. Through a combination of lifestyle modifications, modern technologies, and medication, people can effectively control their illness and lower their risk of problems. As we get closer to possible diabetes treatments, stay up to date on the most recent research and improvements.
Latest Developments in Diabetes Research: Can Diabetes Be Cured?

The effort to cure diabetes has given rise to huge progress in medical research. perhaps while a permanent treatment is still difficult to achieve, advances in technology give hope for improved care and perhaps possible condition reversal. The following are a few of the most hopeful developments in the study of diabetes:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell research is one of the most exciting areas in diabetes research. Scientists are exploring how stem cells can be used to regenerate insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This approach could potentially restore normal insulin production in people with type 1 diabetes. Recent studies have shown progress in differentiating stem cells into insulin-producing cells, bringing us closer to a potential cure.
- Islet Cell Transplantation: Islet cell transplantation involves transferring insulin-producing cells from a donor into a person with diabetes. This procedure has shown promise in helping people with type 1 diabetes achieve insulin independence. Advances in immunosuppressive therapies and encapsulation techniques aim to protect transplanted islet cells from the immune system, improving the longevity and success rate of this treatment.
- Artificial Pancreas: The development of an artificial pancreas represents a significant leap forward in diabetes management. This system combines continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with an insulin pump, automatically adjusting insulin delivery based on real-time blood glucose levels. Recent advancements in algorithms and device integration have improved the accuracy and reliability of artificial pancreas systems, offering better blood sugar control for people with diabetes.
- Gene Editing: Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, hold promise for treating genetic causes of diabetes. Researchers are exploring how to correct genetic defects that lead to type 1 diabetes by editing the DNA of affected cells. Early studies have demonstrated the potential to reprogram cells to produce insulin, paving the way for future gene-based therapies.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy aims to modify the immune system to prevent it from attacking insulin-producing cells in type 1 diabetes. Scientists are developing therapies to target specific immune cells involved in the autoimmune response. Recent clinical trials have shown encouraging results in preserving beta cell function and delaying the progression of type 1 diabetes.
- Gut Microbiome Research: Emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome plays a role in diabetes. Studies have found differences in the gut bacteria of people with diabetes compared to those without the condition. Researchers are investigating how altering the gut microbiome through diet, probiotics, or fecal transplants might influence insulin resistance and blood sugar control, potentially opening new avenues for diabetes treatment.
- Beta Cell Regeneration: In addition to stem cell therapy, scientists are exploring other methods to stimulate the regeneration of beta cells in the pancreas. Small molecules, growth factors, and other biological agents are being tested to promote beta cell proliferation and improve insulin production in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
While the question “can diabetes be cured?” remains unanswered, these latest advances in diabetes research bring us closer to potential cures and better management strategies. Continued investment in research and innovation is essential to turn these promising developments into widely available treatments. By staying informed and supporting ongoing research, we can look forward to a future where diabetes may be a curable condition.
Managing Diabetes Effectively: Can Diabetes Be Cured?

While the search for a cure for diabetes continues, effective management of the condition is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications. Here are some strategies and tips for managing diabetes effectively:
1.Healthy Eating

A balanced diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Consistent Carbohydrate Intake: Monitor and control the intake of carbohydrates, as they directly impact blood sugar levels. Opt for complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- High Fiber Foods: Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as legumes, vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to improve blood sugar control and overall health.
- Healthy Fats: Choose healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, and limit saturated and trans fats.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can spike blood sugar levels.
2.Regular Physical Activity

Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as:
- Walking: A simple and effective way to stay active.Swimming: A low-impact exercise that’s gentle on the joints.
- Cycling: A great way to boost cardiovascular health and manage weight.
- Strength Training: Incorporate resistance exercises like weight lifting or body-weight exercises at least twice a week.
3.Medication Management
Adhering to prescribed medications is vital for controlling diabetes:
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for type 1 diabetes and sometimes required for type 2 diabetes.
- Oral Medications: Type 2 diabetes can be managed with medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, or DPP-4 inhibitors.
- Consult Your Doctor: Regularly review your medication regimen with your healthcare provider to ensure optimal management.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels helps you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and medications.
4.Tools for monitoring include
Glucose Meters: Portable devices that measure blood sugar levels using a small drop of blood.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Devices that provide real-time blood sugar readings and trends, allowing for more precise management.

5.Weight Management

Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly important for people with type 2 diabetes. Effective strategies include:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on nutrient-dense foods and balanced meals.
- Regular Exercise: Stay active to support weight loss and overall health.
- Behavioral Changes: Implement lifestyle changes that promote long-term weight management, such as mindful eating and regular physical activity.
6.Stress Management

Stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Techniques for managing stress include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practice mindfulness or meditation to reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Exercise: Physical activity can help alleviate stress.Hobbies: Engage in activities you enjoy to relax and unwind.
7.Regular Health Checkups
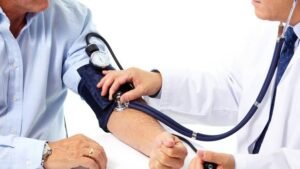
Routine medical appointments are essential for monitoring and managing diabetes complications. Regular checkups should include:
- HbA1c Tests: Measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Blood Pressure Checks: High blood pressure can increase the risk of diabetes complications.
- Cholesterol Tests: Keep cholesterol levels in check to reduce cardiovascular risks.
- Eye Exams: Regular eye exams to monitor for diabetic retinopathy.
- Foot Exams: Regular foot exams to prevent and treat diabetic foot complications.
While we continue to explore the question “can diabetes be cured?” effective management of diabetes is important for maintaining a high quality of life and preventing complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to medication routine, regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, and attending routine health checkups, people with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Stay informed about the latest advancements in diabetes research and treatment options as we move closer to potential cures for diabetes.
10 Essential Tips for Diabetes Patients
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
2. Eat Regularly: Avoid long gaps between meals to prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
3. Sleep Well: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help regulate blood sugar and improve overall health.
4. Keep Track of Your Numbers: Maintain a log of your blood sugar readings, medications, and meals to identify patterns and make informed adjustments.
5. Plan Ahead: Prepare healthy snacks and meals in advance to avoid unhealthy eating choices when you’re busy or on the go.
6. Educate Yourself: Stay informed about diabetes management through credible sources and discuss new findings with your healthcare provider.
7. Be Prepared for Emergencies: Always carry a source of fast-acting glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice, to treat low blood sugar quickly.
8. Communicate with Your Healthcare Team: Regularly update your doctor on your condition and any changes in your symptoms or lifestyle.
9. Limit Alcohol: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation and always with food to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
10. Manage Your Foot Care: Check your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or swelling, and wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes to prevent injuries.
By involving these tips in your daily routine, you can better manage your diabetes and maintain a healthy lifestyle.